1. Some features of advanced mobile phone service are To provide telephone communication to a large number of telephone users within the area of a metropolitan onlyTo use minimum amount of frequency spectrumTo permit hand held as well as vehicle operation of telephone Which of the above are true?
Tags
Show Similar Question And Answers
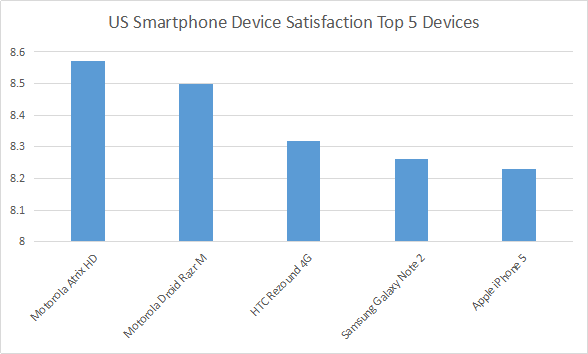 Source: 92.825 US mobile users, July 2012 - January 2013
Fortunately, those questions were answered by OnDevice Research’s representative. He explained that the survey was conducted on mobile web where the survey software could detect the taker’s device and since user’s rate their satisfaction levels on a 1 to 10 scale, thanks to the Nexus device, Google was included.If you analyze the three reports above, which of the following statements would be the best inference?
Source: 92.825 US mobile users, July 2012 - January 2013
Fortunately, those questions were answered by OnDevice Research’s representative. He explained that the survey was conducted on mobile web where the survey software could detect the taker’s device and since user’s rate their satisfaction levels on a 1 to 10 scale, thanks to the Nexus device, Google was included.If you analyze the three reports above, which of the following statements would be the best inference? Powered By:Omega Web Solutions
Powered By:Omega Web Solutions